Since the NPCI introduced the Credit Line on UPI in September 2023, fintech companies have engaged in extensive discussions about how to maximize this opportunity.
A few days back, I came across the insightful white paper published by Zeta on this subject.
I have briefly summarized my understanding of this paper and added a few pointers on possible opportunities on the Product, Innovation, and Revenue front for Banks and Fintechs.
For starters, lets understand
What is the Credit Line on UPI
As per NPCI, Credit Line on UPI: “Pre-sanctioned Credit Line at Banks through UPI” is an innovative financial offering designed to revolutionize the lending landscape. This product empowers individuals and businesses to access pre-sanctioned credit lines from banks. It facilitates the availability of low-ticket, high-volume retail loans, fostering economic growth and enhancing financial inclusion. Leveraging advanced technologies such as data analytics and artificial intelligence, banks can identify credit line opportunities for customers and merchants engaged in significant UPI-based digital payments. Since the customer is going to use UPI in which customer is always connected, available real-time the banks can start from the low-ticket credit lines and go higher up based on consumer behaviour and repayment patterns.
Note*: I have referred to it as “CLOUPI,” for my analysis and ease of reference, not sure if it is an official term for this Product. The white paper refers it as “CLOU”
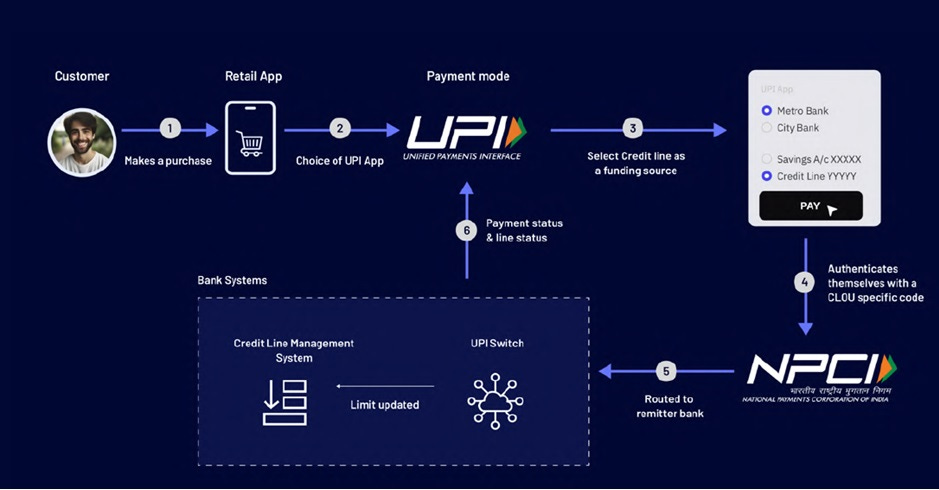
How it works
User Journey as stated in the white paper:
Key Insights and Analysis from the white paper
Introduction: India's Credit Landscape is Poised for Revolution
1. India has significant potential for credit expansion, with only 14-15% retail credit penetration compared to 60-65% in developed economies.
2. The need of the hour is to reimagine the access, availability, and consumption of credit products in a digital-first context.
3. UPI, along with India's digital public infrastructure, has laid the rails for access to the farthest parts of the country and promises a steady, high-fidelity stream of financial data that can transform the inclusion of credit in India.
Credit Line on UPI: A Protocol for Radically Rewiring Credit Distribution
1. “CLOU” allows banks to connect pre-approved credit lines directly to the UPI user base, enabling easier credit access for individuals and businesses.
2. “CLOU” links 160 million underserved credit seekers with the widespread UPI network, removing friction and costs of acquisition, onboarding, disbursal, and collections.
How “CLOU” Will Achieve $1 Trillion Hyperscale
1. “CLOU” adoption will be exponentially higher than other on-demand credit products, riding on UPI rails.
2. Three tailwinds driving “CLOU” growth:
Growth in credit demand,
Shift of digital payments to credit, and
Improvements in the discovery, activation, and utilization of credit.
3. 40% of the P2M transaction base will move from direct bank debits to credit, assuming a 40% credit-to-digital spend ratio.
Identifying the 5 Key “CLOU” Advantages for the Banks
1. Higher activation and utilization by converting loans into credit lines.
2. Operational and cost efficiencies with the digital ecosystem.
3. Data-driven credit assessment to improve access and inclusion.
4. A level playing field for smaller lenders with digital distribution.
5. Dynamic classification of Priority Sector Lending (PSL) to improve achievement of goals.
Achieving 6-Point Implementation Readiness for “CLOU”
1. Compatibility of all platform subsystems with “CLOU”.
2. Scalability to handle significantly increased loan volumes.
3. Flexibility to adapt to product and process innovations.
4. Seamless integration across origination, distribution, and consumption.
5. Robust security and fraud prevention mechanisms.
6. Agile development and deployment capabilities.
Recommendations:
A Framework to Seize the Greenfield Digital Credit Landscape
1. Leverage India's digital public infrastructure, particularly the JAM trinity (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar, Mobile), to enable identification, authentication, and access to creditworthiness data.
2. Collaborate with fintechs to develop innovative credit products and risk assessment models.
3. Innovate on credit provisioning for niche use cases and consumption, such as just-in-time credit, credit at the point of consumption, and embedded and ecosystem-led origination.
I believe following are the Innovation, Product, and Revenue opportunities for fintech companies:
Innovation Opportunities
1. Real-Time Credit Provisioning: Develop systems that enable just-in-time credit access at the point of sale, utilizing the UPI infrastructure for seamless transactions.
2. Alternative Data Utilization: Leverage alternative data sources for credit assessments, allowing for more inclusive lending practices, particularly for thin-file and new-to-credit borrowers.
3. Dynamic Underwriting Models: Create innovative underwriting models that can adapt to various customer segments and real-time data inputs, enhancing the accuracy of creditworthiness evaluations.
4. Embedded Finance Solutions: Explore opportunities for embedded finance by integrating credit offerings within existing platforms, enhancing customer experience and accessibility.
5. Customized Credit Products: Design tailored credit products that cater to specific consumer needs, such as flexible repayment terms and rewards systems linked to usage patterns.
Product Opportunities
1. Credit on UPI (“CLOUPI”): Capitalize on the “CLOUPI” framework to offer pre-approved credit lines linked to UPI, facilitating easy access and management of credit for users.
2. Niche Credit Offerings: Develop credit products targeting underserved segments, such as small-ticket loans for rural consumers or specialized loans for specific sectors like agriculture and renewable energy.
3. Integrated Payment and Credit Solutions: Combine payment processing and credit offerings into a single platform, allowing users to manage transactions and credit seamlessly.
4. Automated Collections and Management Tools: Create tools that automate the loan lifecycle, including repayments, dispute management, and transaction tracking, to enhance operational efficiency.
5. Priority Sector Lending Solutions (PSL): Develop products that dynamically categorize loans based on usage, helping banks meet regulatory requirements while serving priority sectors effectively.
· Priority Sector Lending (PSL) refers to the lending targets set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) for banks and financial institutions to ensure that a certain percentage of their total lending is directed towards specific sectors that are considered important for the economic development of the country. These sectors typically include agriculture, small and medium enterprises (SMEs), education, housing, and others that contribute to the overall growth and welfare of the economy.
Revenue Opportunities
1. Increased Transaction Volume: By facilitating easier access to credit, fintechs can drive higher transaction volumes through UPI, leading to increased revenue from transaction fees.
2. Cross-Selling Opportunities: Leverage customer data to cross-sell additional financial products and services, enhancing customer lifetime value.
3. Partnerships with Banks: Collaborate with banks to offer “CLOUPI” services, creating revenue-sharing models that benefit both parties while expanding market reach.
4. Subscription-Based Models: Introduce subscription services for premium features, such as advanced credit management tools or personalized financial advice.
5. Data Monetization: Utilize aggregated data insights for market research and analytics services, providing valuable information to financial institutions and other stakeholders.
These opportunities highlight the potential for fintech companies to innovate and grow within the evolving credit landscape in India, particularly through the integration of UPI and “CLOUPI” frameworks.